SELU#
Applied element-wise, as:
SELU(x) = scale * (max(0, x) + min(0, α * (exp(x) - 1)))
where:
α = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717
scale = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946
Parameters#
inplace(bool, optional): Can optionally do the operation in-place. Default: False.
Implementation#
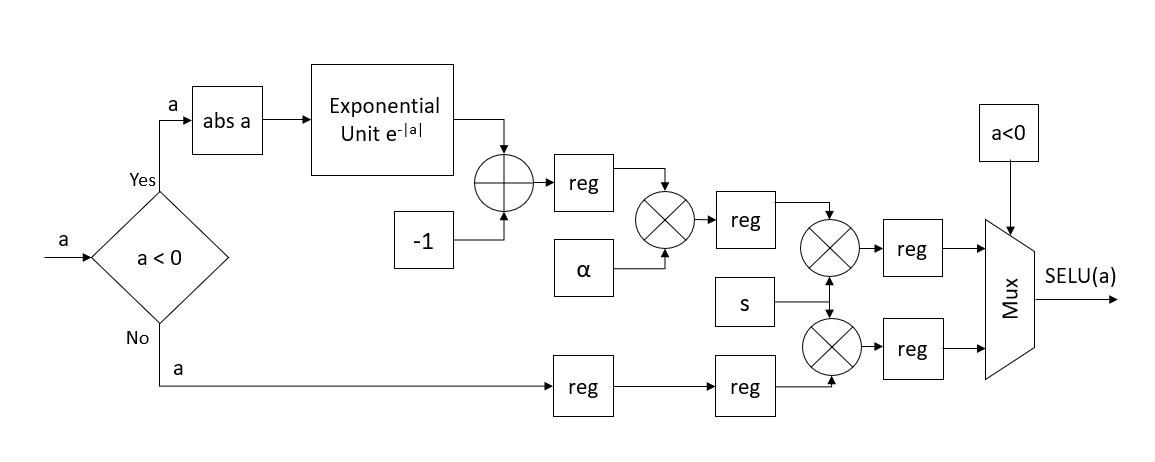
SELU can be represented as per following equation where s is the scale of the exponential linear unit. For the implementation of SELU, initially, exponential function is implemented. Exponential function for a negative real domain (\(\mathbb{R}^-\)), i.e., the function \(e^{-|x|}\) provides a wider scope of optimization as compared to exponential function for the full real domain [2].
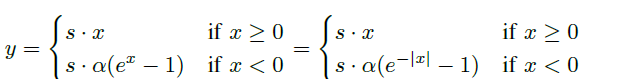
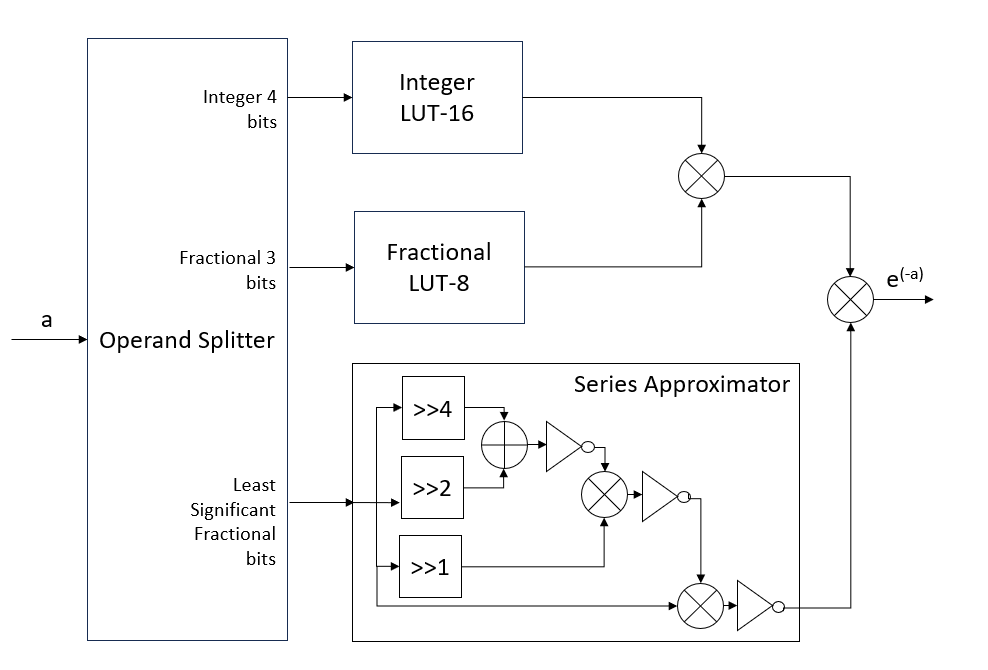
A hybrid approach is used for implementing exponential function \(e^{-|x|}\) for an N-bit binary number as detailed in [2]. Key steps and equations involved are as follows:
Exponential Function Property: Exponential of the sum of two numbers can be written as the product of exponentials of the individual numbers: \(e^{x+y} = e^x \times e^y\)
Representation of Binary Number: The N-bit binary number \(a = b_{N-1}b_{N-2}...b_1b_0\) is represented, where \(b_0\) is the least significant bit, and each bit \(b_i\) has a place value \(p_i\) given by \(p_i = 2^{-P} \times 2^i\).
Exponential Computation: \(e^{-a} = \prod e^{-p_i \times b_i}\)
Saturation and Non-Saturation Regions:
For \(a \geq 16\), the output is saturated to the exponential of \((2^{-P}-16)\).
For the non-saturation region, a hybrid approach is adopted. Input \(a\) is further divided into two ranges:
For values \(> \frac{1}{8}\), Look-Up Tables (LUTs) are used: a 16-word deep LUT for the integer part and an 8-word LUT for the fractional part.
Taylor series expansion is used for values \(\leq \frac{1}{8}\), which is simplified for hardware implementation as in the following equation.
\(e^{-x} = \sim(x \cdot \sim((x \gg 1) \cdot (\sim(x \gg 4 + x \gg 2)))))\)
The implementation consists of three main blocks:
Operand splitter: Divides the input operand into saturation part, integer LUT part, fractional LUT part, and residual part.
Exponential computation for individual parts.
Final stage of multipliers to multiply the computed exponential values of individual parts.
Once exponential has been calculated, SELU is calculated by subtraction and constant multiplications. Flow diagrams for exponential calculation and SELU are given in following figures.