Tanh#
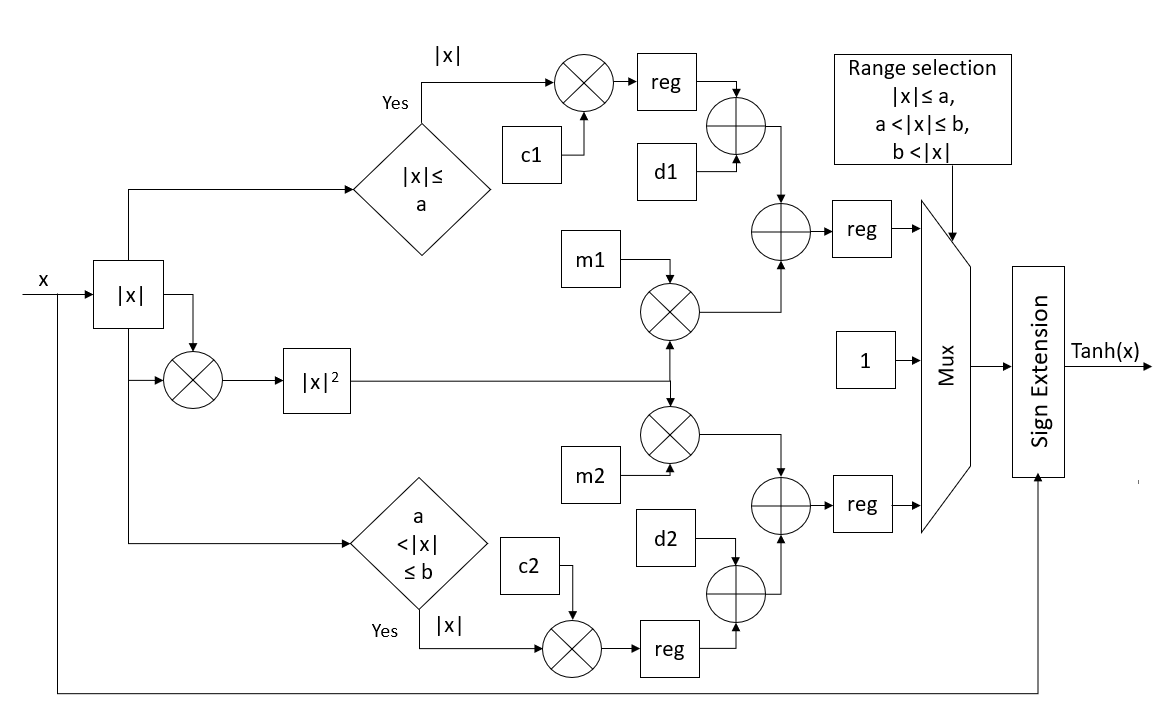
Tanh is defined as:
Tanh(x) = (exp(x) - exp(-x)) / (exp(x) + exp(-x))
This function is applied element-wise.
Implementation#
Hyperbolic tangent is an odd function:
tanh(-x) = -tanh(x)
Using this property, only the absolute value of the input needs to be processed, and the input sign can be directly passed to the output.
Piecewise quadratic approximation is used for tanh activation function as detailed in [3]. In order to preserve the continuity property of the first-order derivative, [3] approximates the first-order derivative of tanh function using piecewise linear approximations. The approximation of the tanh function is then obtained by integrating the approximation of the first-order derivative. The resulting approximation is provided in the following equation, where \(m_1\), \(m_2\), \(c_1\), \(c_2\), \(a\), \(b\), \(d_1\) and \(d_2\) are \(-0.54324\), \(-0.16957\), \(1\), \(0.42654\), \(1.52\), \(2.57\), \(0.016\) and \(0.4519\) respectively.
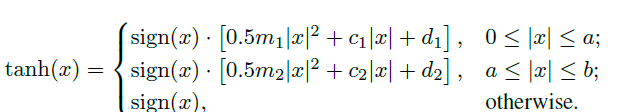
The high-level flow diagram for tanh AF implementation is given in the following figure.