Output Stationary Systolic Module#
The Systolic Array is a widely used architecture for evaluation of the core matrix multiplication. This operation is achieved by the Systolic Module, which consists of a square grid of Processing Elements (PE). Each PE consists of a Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) unit, which takes input features from North and West PEs. Additionally, the incoming features are propagated “forward” and “downwards” to the East and South PEs, respectively. The matrix dimension n is parametrizable at compile time, as well as the arithmetic precision of the operands.
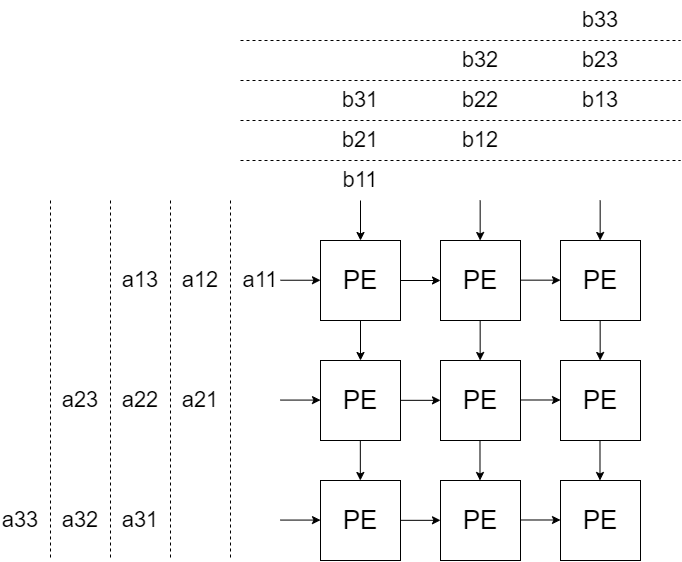
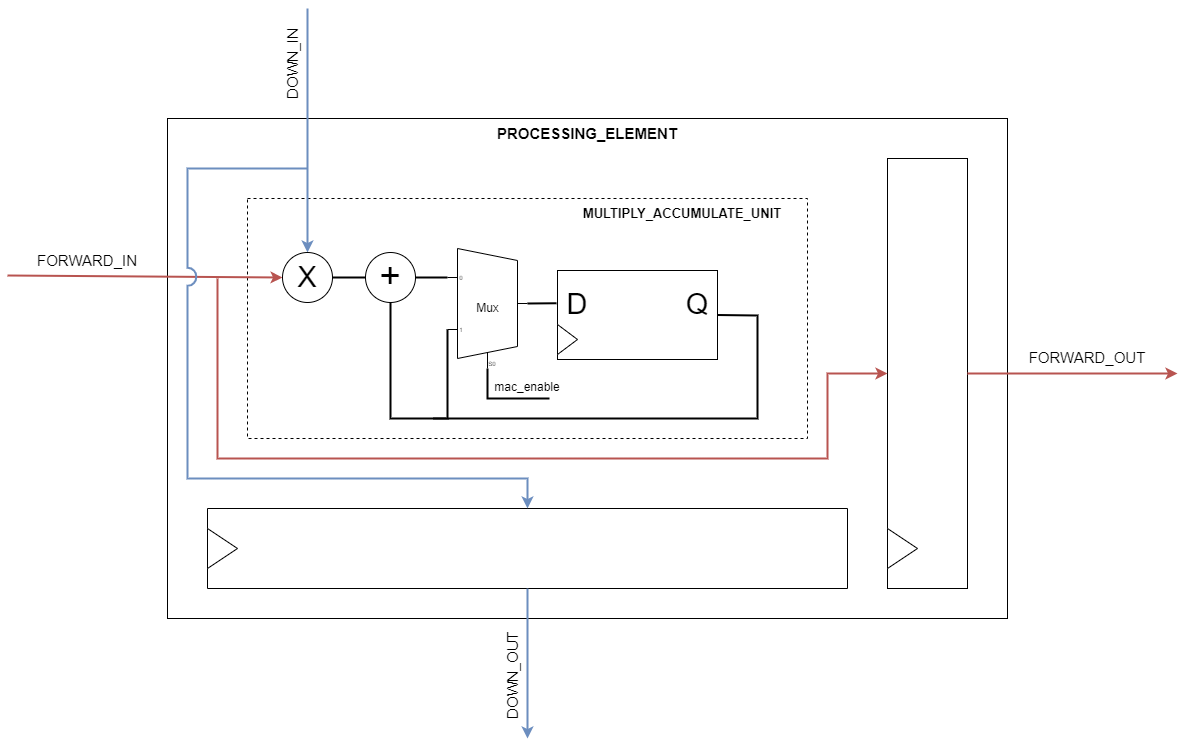
The MAC units in each PE perform the multiply-accumulate operation over 2 cycles, using Xilinx floating-point adders and multipliers. A register is placed after the multiplication stage to meet timing constraints, enabling the systolic module to be operated at 200MHz. In addition to the accumulators, each PE contains a bias adder and an activation core to fully perform the computation required for a Fully-Connected Neural Network layer. After driving the input matrix values, the upstream logic can pulse a bias_valid and then an activation_valid signal to overwrite the accumulator contents with the added bias and activated features, respectively. The activation core supports ReLU and LeakyReLU activations. Finally, the upstream logic can pulse a shift_valid signal to overwrite the accumulators with arbitrary data.
Systolic Module Driver#
The Systolic Module Driver generates pulse signals in the format required to drive the read interface of an on-chip buffer such that data signals are made available with the required timing for the processing elements of a systolic module. This is achieved through a shift register of size BUFFER_SLOT_COUNT. After receiving a starting pulse, the least significant bit is set to 1. Subsequently, the register shifts after every shift pulse, up to a runtime-parametrizable pulse limit count parameter (this is set to the number of output features for the layer being executed). The driver should then pulse a subsequent BUFFER_SLOT_COUNT times until the register is flushed.